Record#
2025-12-1#
修改 qwen_eval prompt 进行新测试
2025-12-2~2025-12-3#
vllm 环境搭建及 debug#
先试了 qwen-2.5-omni 仓库自己给的方法,完全不可行,一看 issue 差评如潮
一个搞笑的,由于他们把根目录占满了,我删除环境的时候报错空间不足还删不了,只能 \rm -rf 掉环境
conda create --prefix /data1/conda/vllm-qwen python=3.10 -y
conda activate /data1/conda/vllm-qwen
export CC=/usr/bin/gcc-9
export CXX=/usr/bin/g++-9
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
pip install xformers==0.0.29.post2 --no-build-isolation
# pip install vllm --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
# 上面直接下好像不行,或者可能得加一个 --torch-backend=auto 来选定 cu118
pip install vllm-0.8.5.post1+cu118-cp38-abi3-manylinux1_x86_64.whl用空闲的卡并配置 modelscope 下载,不过这里用本地模型 model_name = "../cache/modelscope/Qwen/Qwen2.5-Omni-3B",
Qwen2.5-Omni-7B 用 vllm 在 3090 上超显存了,裸模型加载好像就 25G 左右(with flash-attn),等能迁移数据集再换到 77 的上面测(77 上面没空间了已经,或者等后面卡多的时候在75 上并行)
os.environ["VLLM_USE_MODELSCOPE"] = "True"
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1,7"demo 测试(test)#
由于最新提供的 Qwen2.5-omni vllm 示例代码基于较新的 vllm 版本,而在较新的版本中目前还没有对 cu118 进行支持,目前使用的也是旧版的 vllm 库,里面的代码和新代码有点不同
# 这个 convert_image_mode 在旧版 vllm 中是没有的,不过可以直接从新版的代码里面复制过来
# from vllm.multimodal.image import convert_image_mode
# 目前好像用不到这个函数,记录一下先
# from vllm.utils.argparse_utils import FlexibleArgumentParser
from vllm.utils import FlexibleArgumentParser查看 0.8.5.post1 的源码,里面是说当时 V1 版本的 vllm 不支持 use_audio_in_video,设置
os.environ["VLLM_USE_V1"] = "0"llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
dtype=bfloat16,
max_model_len=8192,
max_num_seqs=5,
limit_mm_per_prompt=query_result.limit_mm_per_prompt,
seed=args.seed,
# 默认是 0.8 好像,控制 vllm 分配的 gpu 显存比例
# gpu_memory_utilization=0.6,
# 并行推理开启
# tensor_parallel_size=2,
# enforce_eager=True,
# 使用 modelscope
trust_remote_code=True
)demo 结果:
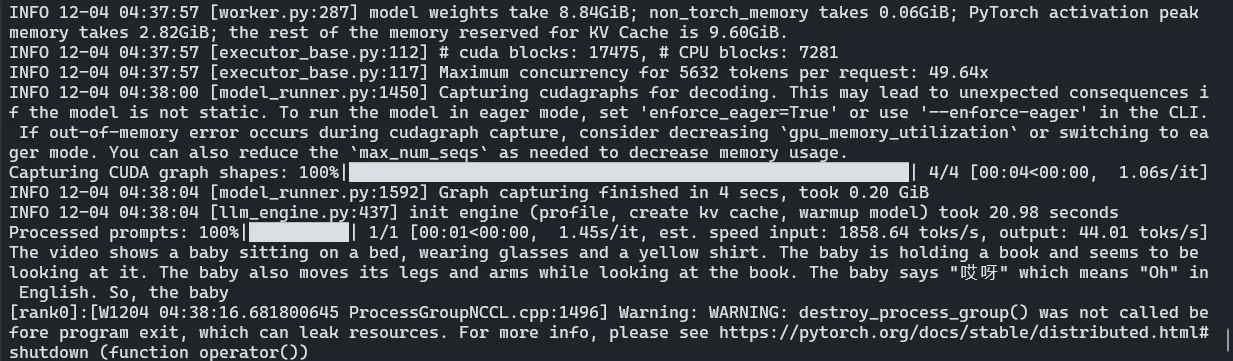
简单并行测试(test)#
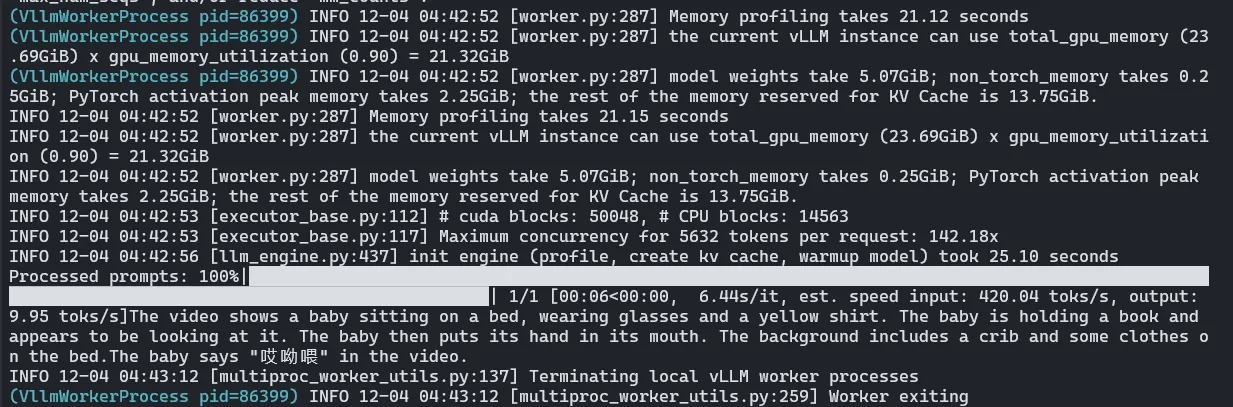
nccl 存在问题,据说 nvidia-nccl-cu11 中的 nccl 是基于 cu110 编译的,无法使用流功能,需要配置 enforce_eager=True(更好的解决方案是重新编译 cu118 的 nccl,或者升级到cu12x)
补充参数:
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
dtype=bfloat16,
max_model_len=8192,
max_num_seqs=5,
limit_mm_per_prompt=query_result.limit_mm_per_prompt,
seed=args.seed,
# 并行推理开启
tensor_parallel_size=2,
enforce_eager=True,
# 使用 modelscope
trust_remote_code=True
)
使用自己的数据,基础测试(test_d, infer)#
vllm 传入的是视频帧的数据,音频是从视频中提取的,根据 vllm/assets/video.py 里面的 VideoAsset(限制帧为 16 来使用固定的样例视频)
重新实现来加载自己的数据(和Qwen2.5-omni一样)
def load_video_frames(path, target_fps=2, temporal_patch_size=2, min_frames=4, max_frames=768):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
if not cap.isOpened():
raise ValueError(f"Could not open video file {path}")
total = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
video_fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) or 0
if video_fps <= 0:
desired = min(total, max_frames)
else:
desired = int(total * target_fps / video_fps)
desired = max(min_frames, min(desired, max_frames, total))
desired = (desired // temporal_patch_size) * temporal_patch_size
desired = max(min_frames, min(desired, total))
idxs = np.linspace(0, total - 1, desired, dtype=int)
frames = []
for i in range(total):
ok = cap.grab()
if not ok:
break
if i in idxs:
ret, frame = cap.retrieve()
if ret:
frames.append(frame)
frames = np.stack(frames)
if len(frames) < desired:
raise ValueError(f"expected {desired} frames, got {len(frames)}")
return frames
def load_audio_from_video(path, sr=16000):
y, _ = librosa.load(path, sr=sr)
return ypython test_d.py --video sample_demo_1.mp4 --question "Describe and transcribe."
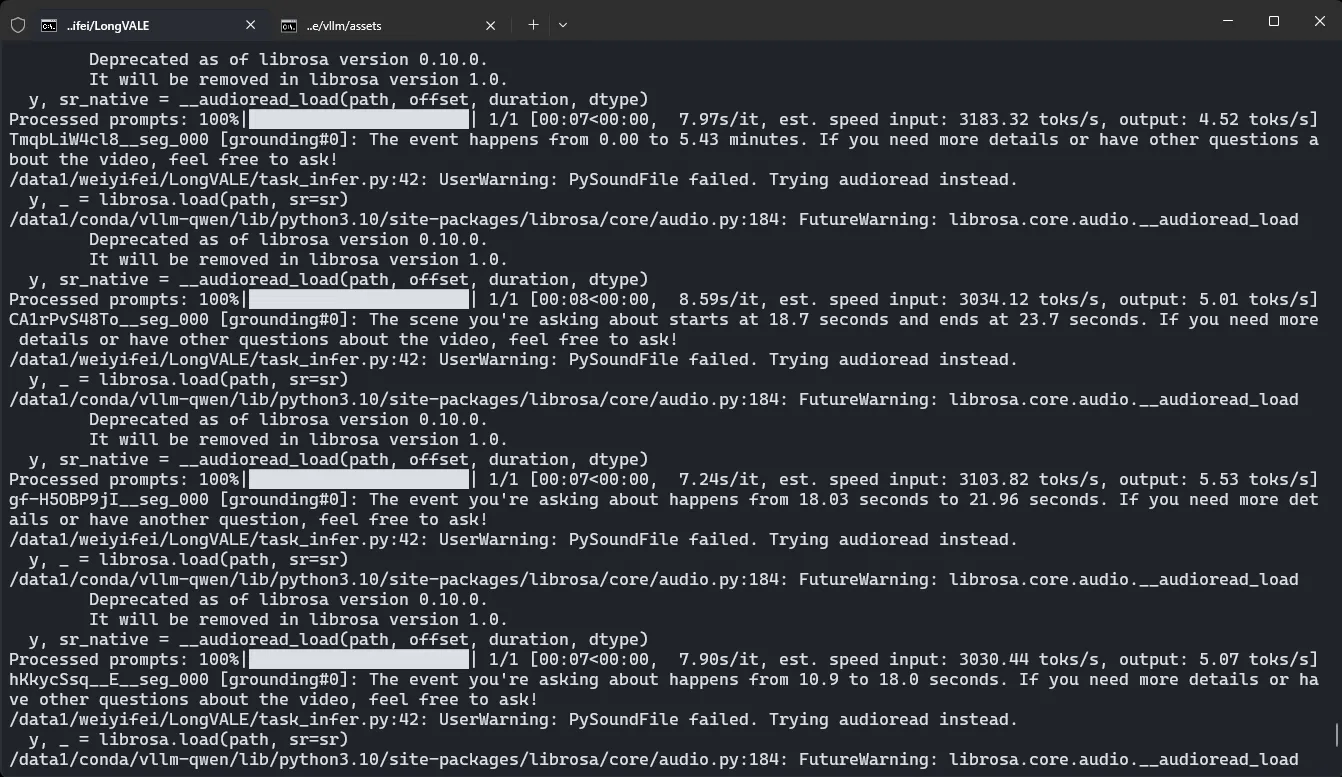
python infer.py --video sample_demo_1.mp4使用自己的数据,完整测试(task_infer)#
基于之前的数据类,修改 infer 以支持从 json 中读视频描述
可能存在的一个问题:会不会超 token 数目,可能要再看看 VL 的部分
python task_infer.py --data-json longvale-annotations-eval-30s.json --video-dir processed/videos --task grounding